7.3 Differentiation of standard functions
General rules
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} \) is the notation for differentiation.
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (y) = \dfrac{dy}{dx} \qquad \dfrac{d}{dx} \big(f(x)\big) = f'(x) \)
When differentiating sums and differences of functions, differentiate them separately.
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} \big(f(x) \pm g(x)\big) = \dfrac{d}{dx} \big(f(x)\big) \pm \dfrac{d}{dx} \big(g(x)\big) = f'(x) \pm g'(x) \)
When differentiating constant multiples of functions, differentiate the function and multiply by the constant.
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} \big(kf(x)\big) = k \dfrac{d}{dx} \big(f(x)\big) = kf'(x) \)
\(\bm{\underline{x^n}} \)
When differentiating \(x^n\), multiply by the power \(n\), then reduce the power \(n\) by \(1\).
This works for all rational values of \(n\), i.e. fractions and negative values.
Tip: Take care when reducing negative powers of \(n\) by \(1\), e.g. \(-2-1=-3\) not \(-1\)!
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (x^n) = nx^{n-1}} \)
When differentiating \(kx\), drop the \(x\). Using the above result:
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (kx) = \dfrac{d}{dx} (kx^1) = 1k\cancel{x^{0}} \)
\(\implies \boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (kx) = k} \)
When differentiating a number \(k\), the result is \(0\). Using the above result:
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (a) = \dfrac{d}{dx} (kx^0) = 0\cancel{kx^{-1}} \)
\(\implies \boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (k) = 0} \)
Exponential functions
Natural logarithmic functions
Trigonometric functions
Tip:
Using the quotient rule, standard results for the reciprocal trigonometric functions can be obtained.
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} \) is the notation for differentiation.
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (y) = \dfrac{dy}{dx} \qquad \dfrac{d}{dx} \big(f(x)\big) = f'(x) \)
When differentiating sums and differences of functions, differentiate them separately.
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} \big(f(x) \pm g(x)\big) = \dfrac{d}{dx} \big(f(x)\big) \pm \dfrac{d}{dx} \big(g(x)\big) = f'(x) \pm g'(x) \)
When differentiating constant multiples of functions, differentiate the function and multiply by the constant.
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} \big(kf(x)\big) = k \dfrac{d}{dx} \big(f(x)\big) = kf'(x) \)
\(\bm{\underline{x^n}} \)
When differentiating \(x^n\), multiply by the power \(n\), then reduce the power \(n\) by \(1\).
This works for all rational values of \(n\), i.e. fractions and negative values.
Tip: Take care when reducing negative powers of \(n\) by \(1\), e.g. \(-2-1=-3\) not \(-1\)!
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (x^n) = nx^{n-1}} \)
When differentiating \(kx\), drop the \(x\). Using the above result:
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (kx) = \dfrac{d}{dx} (kx^1) = 1k\cancel{x^{0}} \)
\(\implies \boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (kx) = k} \)
When differentiating a number \(k\), the result is \(0\). Using the above result:
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (a) = \dfrac{d}{dx} (kx^0) = 0\cancel{kx^{-1}} \)
\(\implies \boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (k) = 0} \)
Exponential functions
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (e^x) = e^x} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (a^x) = a^x\ln{a}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (a^x) = a^x\ln{a}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (e^{kx}) = ke^{kx}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (a^{kx}) = ka^{kx}\ln{a}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (a^{kx}) = ka^{kx}\ln{a}} \)
Natural logarithmic functions
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\ln{x}) = \dfrac{1}{x}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\ln{kx}) = \dfrac{1}{x}} \)
Trigonometric functions
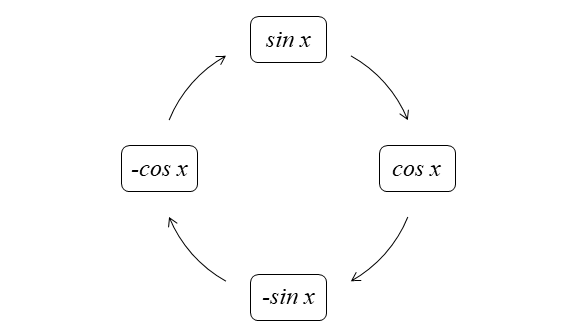
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\sin{x}) = \cos{x}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cos{x}) = -\sin{x}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\tan{x}) = \sec^2{x}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cos{x}) = -\sin{x}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\tan{x}) = \sec^2{x}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\sin{kx}) = k\cos{kx}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cos{kx}) = -k\sin{kx}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\tan{kx}) = k\sec^2{kx}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cos{kx}) = -k\sin{kx}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\tan{kx}) = k\sec^2{kx}} \)
Tip:

Using the quotient rule, standard results for the reciprocal trigonometric functions can be obtained.
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\sec{x}) = \sec{x}\tan{x}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cosec{x}) = -\cosec{x}\cot{x}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cot{x}) = -\cosec^2{x}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cosec{x}) = -\cosec{x}\cot{x}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cot{x}) = -\cosec^2{x}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\sec{kx}) = k\sec{kx}\tan{kx}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cosec{kx}) = -k\cosec{kx}\cot{kx}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cot{kx}) = -k\cosec^2{kx}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cosec{kx}) = -k\cosec{kx}\cot{kx}} \)
\(\boxed{\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cot{kx}) = -k\cosec^2{kx}} \)
Important
Standard differentiation results
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (x^n) = nx^{n-1} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (e^{kx}) = ke^{kx} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (a^{kx}) = ka^{kx}\ln{a} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\ln{kx}) = \dfrac{1}{x} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\sin{kx}) = k\cos{kx} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cos{kx}) = -k\sin{kx} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\tan{kx}) = k\sec^2{kx} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\sec{kx}) = k\sec{kx}\tan{kx} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cosec{kx}) = -k\cosec{kx}\cot{kx} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cot{kx}) = -k\cosec^2{kx} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (x^n) = nx^{n-1} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (e^{kx}) = ke^{kx} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (a^{kx}) = ka^{kx}\ln{a} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\ln{kx}) = \dfrac{1}{x} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\sin{kx}) = k\cos{kx} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cos{kx}) = -k\sin{kx} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\tan{kx}) = k\sec^2{kx} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\sec{kx}) = k\sec{kx}\tan{kx} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cosec{kx}) = -k\cosec{kx}\cot{kx} \)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx} (\cot{kx}) = -k\cosec^2{kx} \)
3