10.3 Vector addition and multiplication by a scalar
Vector addition
Triangle law for vector addition:
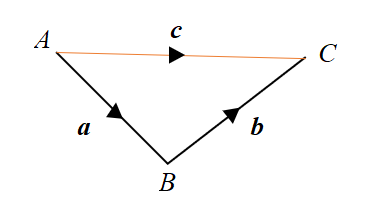
\(\overrightarrow{AB} + \overrightarrow{BC} = \overrightarrow{AC} \)
If \(\overrightarrow{AB} = \bold{a}\), \(\overrightarrow{BC} = \bold{b}\) and \(\overrightarrow{AC} = \bold{c}\), then:
\(\bold{a} + \bold{b} = \bold{c} \)
Parallelogram law for vector addition:
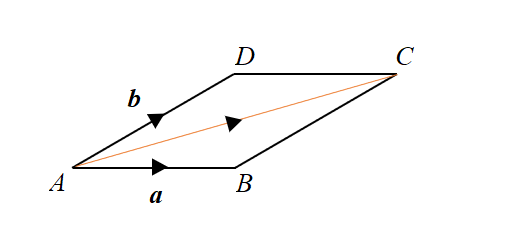
\(\overrightarrow{AB} + \overrightarrow{BC} = \overrightarrow{AC} \)
\(\overrightarrow{BC} = \overrightarrow{AD} \)
\(\implies \bold{a} + \bold{b} = \overrightarrow{AC} \)
In column vector form:
\(\begin{pmatrix} p \\ q \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix} r \\ s \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} p+r \\ q+s \end{pmatrix} \)
Vector subtraction
Subtracting a vector is the equivalent of adding the reverse of a vector
\(\bold{a} - \bold{b} = \bold{a} + (-\bold{b}) \)
Multiplication by a scalar
\(\lambda \begin{pmatrix} p \\ q \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} \lambda p \\ \lambda q \end{pmatrix} \)
Triangle law for vector addition:

\(\overrightarrow{AB} + \overrightarrow{BC} = \overrightarrow{AC} \)
If \(\overrightarrow{AB} = \bold{a}\), \(\overrightarrow{BC} = \bold{b}\) and \(\overrightarrow{AC} = \bold{c}\), then:
\(\bold{a} + \bold{b} = \bold{c} \)
Parallelogram law for vector addition:

\(\overrightarrow{AB} + \overrightarrow{BC} = \overrightarrow{AC} \)
\(\overrightarrow{BC} = \overrightarrow{AD} \)
\(\implies \bold{a} + \bold{b} = \overrightarrow{AC} \)
In column vector form:
\(\begin{pmatrix} p \\ q \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix} r \\ s \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} p+r \\ q+s \end{pmatrix} \)
Vector subtraction
Subtracting a vector is the equivalent of adding the reverse of a vector
\(\bold{a} - \bold{b} = \bold{a} + (-\bold{b}) \)
Multiplication by a scalar
\(\lambda \begin{pmatrix} p \\ q \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} \lambda p \\ \lambda q \end{pmatrix} \)
3