17.8 Projectiles
A particle moving in a vertical plane under the action of gravity is known as a projectile.
Horizontal projection
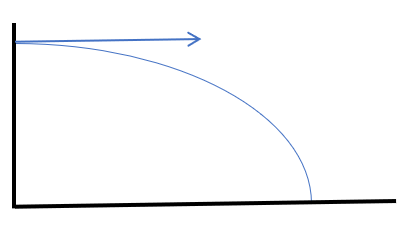
The horizontal motion of a projectile is modelled as having constant velocity (\(a = 0\)).
The forumla \(s = vt\) can be used.
The vertical motion of a projectile is modelled as having constant acceleration due to gravity (\(a = g\)).
The \(suvat\) equations can be used.
Unless otherwise stated, use \(g\) = 9.8 ms-2.
Projection at an angle
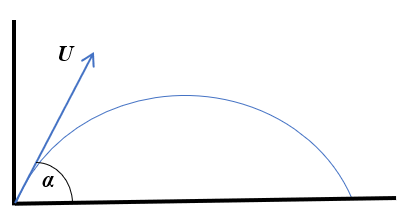
A particle is projected with initial velocity U at an angle α above the horizontal.
The velocity can be resolved into horizontal and vertical components:
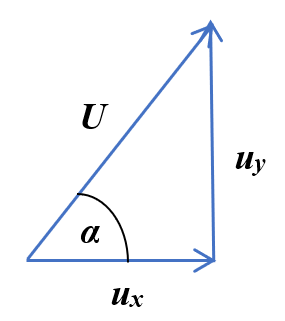
\(\cos{α} = \dfrac{u_x}{U} \implies u_x = U\cos{α} \)
\(\sin{α} = \dfrac{u_y}{U} \implies u_y = U\sin{α} \)
The horizontal component of the initial velocity is \(U\cos{α}\).
The vertical component of the initial velocity is \(U\sin{α}\).
A projectile reaches its maximum height when the vertical component of its velocity is equal to 0.
Horizontal projection

The horizontal motion of a projectile is modelled as having constant velocity (\(a = 0\)).
The forumla \(s = vt\) can be used.
The vertical motion of a projectile is modelled as having constant acceleration due to gravity (\(a = g\)).
The \(suvat\) equations can be used.
Unless otherwise stated, use \(g\) = 9.8 ms-2.
Projection at an angle

A particle is projected with initial velocity U at an angle α above the horizontal.
The velocity can be resolved into horizontal and vertical components:

\(\cos{α} = \dfrac{u_x}{U} \implies u_x = U\cos{α} \)
\(\sin{α} = \dfrac{u_y}{U} \implies u_y = U\sin{α} \)
The horizontal component of the initial velocity is \(U\cos{α}\).
The vertical component of the initial velocity is \(U\sin{α}\).
A projectile reaches its maximum height when the vertical component of its velocity is equal to 0.
3