#CD(a)
how some dyes attach themselves to fibres in terms of intermolecular bonds, ionic bonds and covalent bonding
Details of dye structures will be given.
#CD(b)
the structure of a dye molecule in terms of the chromophore and:
(i) functional groups that modify the chromophore
(ii) functional groups that affect the solubility of the dye
(iii) functional groups that allow the dye to bond to fibres
#CD(c)
fats and oils consist mainly of mixed esters of propane-1,2,3-triol with varying degrees of unsaturation
#CD(d)
the formulae of arenes and their derivatives (aromatic compounds):
(i) the delocalisation of electrons in these compounds
(ii) how delocalisation accounts for their characteristic properties
Limited to undergoing substitution (often slowly) rather than addition reactions in (ii).
#CD(e)
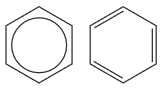
the two common representations of the benzene molecule and their relation to:
(i) the shape of the molecule
(ii) bonding in the molecule (including a treatment of enthalpy change of hydrogenation)
The common representations to be considered are:
#CD(f)
naming the individual functional groups mentioned elsewhere in the specification within a polyfunctional molecule and making predictions about the properties of the polyfunctional molecule;
testing for these functional groups in a compound, using reactions mentioned in the specification
#CD(g)
the following electrophilic substitution reactions of arenes and the names of the benzene derivatives formed:
(i) halogenation of the ring
(ii) nitration, including the mechanism
(iii) sulfonation
(iv) Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation
Naming of acylated products is not required.
#CD(h)
the formation of diazonium compounds and the coupling reactions that these undergo to form azo dyes
#CD(i)
the following reactions involving carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones):
(i) oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids using acidified dichromate, under reflux
(ii) reaction with Fehling’s solution and Tollens' reagent
(iii) reaction with cyanide ions to form the cyanohydrin
Formulae of (all) products required, but not equations.
#CD(j)
use of organic reactions and reaction conditions mentioned here and elsewhere in the specification to suggest and explain synthetic routes for preparing organic compounds
Further reactions that learners are expected to consider are given on the Data Sheet.
#CD(k)
the mechanism of the nucleophilic addition reaction between a carbonyl compound and CN-, using ‘curly arrows’ and partial charges
#CD(l)
organic mechanisms:
(i) use of the following terms to classify organic reactions: addition, condensation, elimination, substitution, oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis
(ii) use of ‘curly arrows’ and partial charges, where appropriate, to describe unfamiliar mechanisms, given appropriate information
#CD(m)
the origins of colour (and UV absorption) in organic molecules
In terms of:
- transitions between electronic energy levels
- the relationship between the extent of delocalisation in the chromophore and the energy absorbed.
#CD(n)
the general principles of gas–liquid chromatography:
(i) sample injected into inert carrier gas stream
(ii) column consisting of high boiling liquid on porous support
(iii) detection of the emerging compounds (sometimes involving mass spectrometry)
(iv) distinguishing compounds by their retention times