#1.6.1
A single molecule of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleotide derivative and is formed from a molecule of ribose, a molecule of adenine and three phosphate groups.
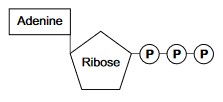
#1.6.2
Hydrolysis of ATP to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and an inorganic phosphate group (Pi) is catalysed by the enzyme ATP hydrolase.
#1.6.3
The hydrolysis of ATP can be coupled to energy-requiring reactions within cells.
#1.6.4
The inorganic phosphate released during the hydrolysis of ATP can be used to phosphorylate other compounds, often making them more reactive.
#1.6.5
ATP is resynthesised by the condensation of ADP and Pi. This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme ATP synthase during photosynthesis, or during respiration.