#1.5.1.1
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are important information-carrying molecules. In all living cells, DNA holds genetic information and RNA transfers genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes.
#1.5.1.2
Ribosomes are formed from RNA and proteins.
#1.5.1.3
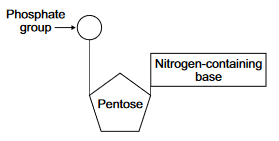
Both DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is formed from a pentose, a nitrogen-containing organic base and a phosphate group:
#1.5.1.4
The components of a DNA nucleotide are deoxyribose, a phosphate group and one of the organic bases adenine, cytosine, guanine or thymine.
#1.5.1.5
The components of an RNA nucleotide are ribose, a phosphate group and one of the organic bases adenine, cytosine, guanine or uracil.
#1.5.1.6
A condensation reaction between two nucleotides forms a phosphodiester bond.
#1.5.1.7
A DNA molecule is a double helix with two polynucleotide chains held together by hydrogen bonds between specific complementary base pairs.
#1.5.1.8
An RNA molecule is a relatively short polynucleotide chain.
#1.5.1.9
Students should be able to appreciate that the relative simplicity of DNA led many scientists to doubt that it carried the genetic code.